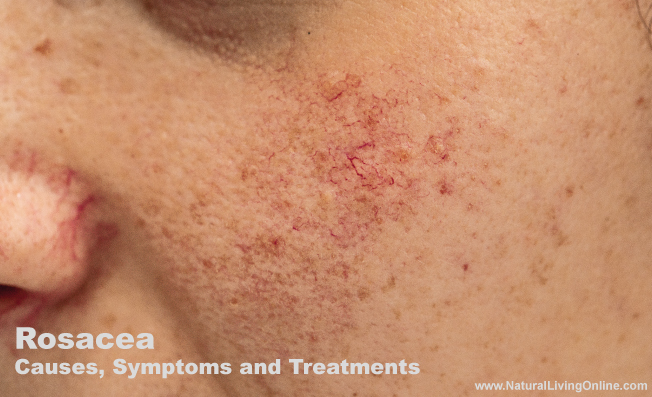
Rosacea is a chronic skin condition that causes redness, inflammation, and pimple-like bumps on the face. It affects more than 16 million Americans and is more common in fair-skinned individuals. Rosacea typically develops in adults between the ages of 30 and 50, and it’s more prevalent in women.
Clinical Signs and Symptoms
The clinical signs and symptoms of rosacea may vary from person to person, but the most common include:
- Facial redness: Persistent facial redness, often in the central part of the face, including the cheeks, nose, chin, and forehead.
- Visible blood vessels: Small, visible blood vessels on the face, known as telangiectasias.
- Swelling: Swelling and inflammation of the affected area, leading to a swollen or bulbous nose, a condition known as rhinophyma.
- Pimples and bumps: Small red bumps or pustules on the skin, often resembling acne.
- Burning or stinging: A burning or stinging sensation on the skin.
- Eye problems: Some people with rosacea may experience eye irritation, redness, or dryness.
- Flushing: Sudden, brief episodes of facial redness or flushing that may be triggered by certain foods, drinks, or emotions.
Causes of Rosacea
The exact cause of rosacea is unknown. However, researchers have identified several factors that can contribute to its development, including:
- Genetics: Rosacea tends to run in families, suggesting a genetic predisposition.
- Demodex mites: These microscopic mites live on the skin and hair follicles and are more prevalent in individuals with rosacea.
- Immune system dysfunction: Some research suggests that immune system dysfunction may contribute to rosacea development.
- Lifestyle Factors: Lifestyle factors can also play a role in the development and worsening of rosacea symptoms. Some lifestyle factors that may contribute to rosacea include:
- Sun exposure: Exposure to the sun can trigger and worsen rosacea symptoms. It’s important to wear sunscreen daily and avoid prolonged sun exposure.
- Hot drinks: Hot drinks, such as coffee and tea, can cause blood vessels in the face to dilate, which can lead to redness and flushing.
- Spicy foods: Spicy foods can also cause blood vessels to dilate, leading to redness and flushing. It’s best to avoid spicy foods if you have rosacea.
- Alcohol: Alcohol can cause blood vessels in the face to dilate, leading to redness and flushing. It’s best to avoid alcohol if you have rosacea, or limit your intake to one drink per day.
- Extreme temperatures: Exposure to extreme temperatures, such as hot or cold weather, can trigger and worsen rosacea symptoms. It’s important to dress appropriately for the weather and avoid extreme temperatures whenever possible.
- Stress: Stress can trigger and worsen rosacea symptoms. Finding ways to manage stress, such as through exercise, meditation, or therapy, can be helpful in managing rosacea symptoms.
- Harsh skincare products: Skincare products that contain harsh chemicals, fragrances, or exfoliants can irritate the skin and worsen rosacea symptoms. It’s best to use gentle skincare products that are free of irritants.
- By avoiding triggers and making lifestyle changes, you can help manage your rosacea symptoms and improve your quality of life. If you have questions about how to manage your rosacea, talk to your dermatologist for advice and guidance.
- Environmental factors: Sun exposure, extreme temperatures, hot drinks, alcohol, spicy foods, and stress can all trigger or worsen rosacea symptoms.
- Blood vessel abnormalities: Some research indicates that abnormalities in blood vessels on the face may contribute to rosacea development.
Treatment Options for Rosacea
While there is no cure for rosacea, there are various treatment options available to manage symptoms. Treatment plans vary depending on the severity of the condition and individual patient needs.
- Topical medications: Prescription topical medications such as azelaic acid, metronidazole, or ivermectin may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and redness. These medications are typically applied to the affected areas once or twice daily.
- Oral antibiotics: In more severe cases, oral antibiotics such as tetracycline or doxycycline may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and kill bacteria. These medications may be taken for several weeks or months.
- Laser therapy: In some cases, laser therapy may be used to reduce redness and visible blood vessels. Laser therapy works by targeting blood vessels in the affected areas and causing them to shrink.
- Lifestyle changes: Avoiding triggers such as sun exposure, hot drinks, alcohol, spicy foods, and stress can help reduce rosacea symptoms. Wearing sunscreen daily and avoiding extreme temperatures can also be helpful.
- Skincare routine: Gentle skincare products that are free of fragrance and harsh chemicals can help reduce irritation and inflammation. Moisturizing regularly can also help keep the skin hydrated and reduce redness.
Rosacea Natural Treatment Options
While there is no known cure for rosacea, there are several natural treatment options that may help manage symptoms and prevent flare-ups. In this blog post, we’ll explore some of the most effective natural treatments for rosacea.
Aloe Vera
Aloe vera is a natural anti-inflammatory agent that can help soothe irritated skin. Apply aloe vera gel directly to the affected area to help reduce redness and inflammation. You can also try using aloe vera-based skincare products, such as creams or lotions, to help prevent flare-ups.
Green Tea
Green tea is a natural anti-inflammatory agent that can help reduce redness and inflammation in the skin. Drinking green tea regularly can help reduce the severity of rosacea symptoms, and applying green tea extract topically may help soothe irritated skin.
Probiotics
Probiotics are live bacteria and yeasts that are good for your health, especially your digestive system. Some studies have shown that taking probiotic supplements may help reduce the severity of rosacea symptoms. Eating foods that are naturally rich in probiotics, such as yogurt and kefir, may also be beneficial.
Chamomile
Chamomile is a natural anti-inflammatory agent that can help soothe irritated skin. You can brew chamomile tea and apply it directly to the affected area, or try using skincare products that contain chamomile extract.
Licorice Root
Licorice root contains compounds that have anti-inflammatory and skin-soothing properties. Applying licorice root extract topically may help reduce redness and inflammation in the skin.
Honey
Honey has natural antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties that can help soothe and heal irritated skin. Apply a small amount of honey to the affected area and leave it on for 10-15 minutes before rinsing off with warm water.
Oatmeal
Oatmeal is a natural skin-soothing agent that can help reduce redness and inflammation in the skin. You can add oatmeal to your bathwater, or try using skincare products that contain colloidal oatmeal.
In conclusion, rosacea is a chronic skin condition that affects millions of Americans. While there is no known cure for rosacea, there are several natural treatment options that can help manage symptoms and prevent flare-ups. Incorporating these natural remedies into your skincare routine, along with proper diet and lifestyle changes, can help you achieve clearer, healthier-looking skin. However, it’s important to remember that everyone’s skin is different, and what works for one person may not work for another. If you have severe or persistent rosacea symptoms, it’s important to consult with a dermatologist or healthcare professional for personalized treatment recommendations.
References
- van Zuuren EJ. Rosacea. N Engl J Med. 2017 Nov 02;377(18):1754-1764.
- Ahn CS, Huang WW. Rosacea Pathogenesis. Dermatol Clin. 2018 Apr;36(2):81-86.
- Rainer BM, Kang S, Chien AL. Rosacea: Epidemiology, pathogenesis, and treatment. Dermatoendocrinol. 2017;9(1):e1361574.
- Gravina A, Federico A, Ruocco E, Lo Schiavo A, Masarone M, Tuccillo C, Peccerillo F, Miranda A, Romano L, de Sio C, de Sio I, Persico M, Ruocco V, Riegler G, Loguercio C, Romano M. Helicobacter pylori infection but not small intestinal bacterial overgrowth may play a pathogenic role in rosacea. United European Gastroenterol J. 2015 Feb;3(1):17-24.
- Wang YA, James WD. Update on rosacea classification and its controversies. Cutis. 2019 Jul;104(1):70-73.
This website does not provide medical advice.
All information provided on this website, and on associated social media networks, including but not limited to texts, images, and numbers are for general information purpose only. It is not intended as medical advice and it does not include all possible precautions, side effects, or interactions that may occur. Neither NaturalLivingOnline.com nor its author/founder take responsibility for how you use this information. Statements contained on NaturalLivingOnline.com have not been evaluated by the FDA. You should conduct thorough research via multiple sources and consult your physician or qualified doctor before using any essential oil or herbal remedy. Information on NaturalLivingOnline.com must not be relied upon for medical, legal, financial or other decisions.