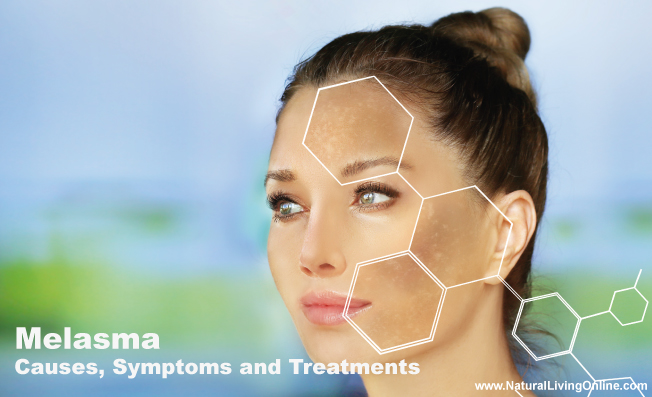
Melasma is a common skin condition that causes dark, discolored patches to appear on the face, particularly on the cheeks, forehead, nose, and upper lip. The condition affects both men and women, but is more common in women and is often associated with hormonal changes. While melasma is not a serious medical condition, it can cause significant distress and affect self-esteem. In this article, we will discuss the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for melasma.
Causes of Melasma
The exact causes of melasma are not well understood, but there are several factors that can contribute to the development of the condition. The most common causes of melasma are:
Hormonal changes
Melasma is often associated with hormonal changes, particularly during pregnancy and menopause. The condition is also more common in women who take oral contraceptives or hormone replacement therapy.
Sun exposure
Exposure to the sun can trigger or worsen melasma, as ultraviolet (UV) rays can stimulate the production of melanin, the pigment that gives color to the skin.
Genetics
Melasma is more common in individuals with a family history of the condition.
Skin type
People with darker skin tones, particularly those of Hispanic, Asian, or African descent, are more prone to developing melasma.
Clinical Signs and Symptoms
Melasma is a common skin condition that causes patches of brown or grayish-brown discoloration on the face, particularly on the cheeks, forehead, nose, and upper lip. The discoloration is caused by an increase in the production of melanin, the pigment that gives color to the skin. The following are the clinical signs and symptoms of melasma:
Hyperpigmented patches: The most common symptom of melasma is the appearance of hyperpigmented patches on the face. These patches can be brown, gray, or tan in color and may be symmetrical on both sides of the face.
Irregular shape and size
The patches of discoloration caused by melasma are often irregular in shape and size, and may have a blotchy or spotty appearance.
Location
The patches of discoloration usually occur on the cheeks, forehead, nose, and upper lip. They may also appear on other parts of the body that are frequently exposed to the sun, such as the neck and forearms.
Sun exposure
Sun exposure is a major factor that can trigger or worsen melasma. The patches of discoloration may become more pronounced after exposure to the sun or after using tanning beds.
Pregnancy
Melasma is sometimes called the “mask of pregnancy” because it is a common symptom during pregnancy. It can also occur in women who take birth control pills or hormone replacement therapy.
Other symptoms
Melasma does not cause any other symptoms such as itching or pain. However, the patches of discoloration can cause significant emotional distress and self-consciousness in some people.
It Is important to consult a dermatologist if you experience any of these symptoms. A dermatologist can diagnose melasma based on a visual examination of the skin and may recommend treatment options to help improve the appearance of the skin.
Treatment
While melasma is not a serious medical condition, it can cause significant distress and affect self-esteem. There are several treatment options available to help improve the appearance of melasma. These include:
Sun protection
Protecting the skin from the sun is crucial for preventing the development or worsening of melasma. Be sure to wear sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30 and avoid prolonged exposure to the sun, particularly during peak hours.
Topical treatments
There are several topical treatments available for melasma, including hydroquinone, retinoids, and corticosteroids. These medications work by reducing the production of melanin in the skin, which helps to lighten the dark patches. It is important to note that these medications can cause skin irritation and should only be used under the supervision of a dermatologist.
Chemical peels
Chemical peels involve applying a chemical solution to the skin, which causes the top layer of skin to peel off. This can help to lighten the dark patches of melasma and improve the overall appearance of the skin. Chemical peels can be performed by a dermatologist or esthetician.
Microdermabrasion
Microdermabrasion involves using a device to gently exfoliate the skin, which can help to lighten the dark patches of melasma. This treatment is typically performed by a dermatologist or esthetician.
Laser therapy
Laser therapy involves using a laser to target and break up the pigment in the skin. This treatment can be effective for improving the appearance of melasma, but may require multiple sessions and can cause skin irritation and redness.
Cosmetics
There are several cosmetics available that can help to conceal the dark patches of melasma, such as color-correcting makeup and tinted moisturizers.
Home Remedies
While there are many medical treatments available for melasma, there are also several natural remedies that may help improve the appearance of the dark patches on the skin. Here are some home remedies that may be effective in treating melasma:
Aloe Vera
Aloe vera is a natural ingredient that has anti-inflammatory properties and can help to soothe the skin. Applying fresh aloe vera gel to the affected areas can help to reduce inflammation and lighten the dark patches over time.
Apple cider vinegar
Apple cider vinegar is a natural skin lightener that can help to reduce the appearance of melasma. Dilute apple cider vinegar with water in a 1:1 ratio and apply to the affected areas with a cotton ball. Leave on for a few minutes before rinsing off with water.
Lemon juice
Lemon juice is another natural skin lightener that can help to reduce the appearance of melasma. Apply fresh lemon juice to the affected areas with a cotton ball and leave on for 10-15 minutes before rinsing off with water. It is important to note that lemon juice can cause skin irritation and should be used with caution.
Turmeric
Turmeric is a natural ingredient that has anti-inflammatory properties and can help to reduce the appearance of melasma. Mix turmeric powder with water to form a paste and apply to the affected areas. Leave on for 15-20 minutes before rinsing off with water.
Milk
Milk contains lactic acid, which can help to exfoliate the skin and lighten the dark patches of melasma. Soak a cotton ball in milk and apply to the affected areas. Leave on for 15-20 minutes before rinsing off with water.
Papaya
Papaya contains an enzyme called papain, which can help to exfoliate the skin and lighten the dark patches of melasma. Mash a ripe papaya and apply to the affected areas. Leave on for 15-20 minutes before rinsing off with water.
Onion juice
Onion juice contains sulfur compounds that can help lighten the skin and reduce the appearance of melasma. To use it, grate an onion and extract the juice. Apply the juice on the affected area using a cotton ball and leave it on for 10-15 minutes before rinsing it off with water. Repeat this process once a day for a few weeks.
Green tea
Green tea contains antioxidants that can help reduce the appearance of melasma. To use it, brew a cup of green tea and let it cool down. Apply the cooled tea on the affected area using a cotton ball and leave it on for 10-15 minutes before rinsing it off with water. Repeat this process once a day for a few weeks.
It Is important to note that these home remedies may take several weeks or even months to show results and may not be as effective as medical treatments. It is always important to talk to a dermatologist before trying any home remedies, particularly if you have sensitive skin or are prone to allergic reactions.
In conclusion, melasma is a common skin condition that affects many people, especially women. While it is not a serious health concern, it can be distressing for those who have it. Fortunately, there are many medical and natural remedies available to treat melasma. Medical treatments such as topical creams, chemical peels, and laser therapy have been shown to be effective in reducing the appearance of melasma. However, these treatments can be expensive and may have side effects.
References
- Yeung H, Kahn B, Ly BC, Tangpricha V. Dermatologic Conditions in Transgender Populations. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2019 Jun;48(2):429-440.
- Ching D, Amini E, Harvey NT, Wood BA, Mesbah Ardakani N. Cutaneous tumoural melanosis: a presentation of complete regression of cutaneous melanoma. Pathology. 2019 Jun;51(4):399-404.
- Roberts WE, Henry M, Burgess C, Saedi N, Chilukuri S, Campbell-Chambers DA. Laser Treatment of Skin of Color for Medical and Aesthetic Uses With a New 650-Microsecond Nd:YAG 1064nm Laser. J Drugs Dermatol. 2019 Apr 01;18(4):s135-137.
- Rendon MI. Hyperpigmentation Disorders in Hispanic Population in the United States. J Drugs Dermatol. 2019 Mar 01;18(3):s112-114.
- Zubair R, Lyons AB, Vellaichamy G, Peacock A, Hamzavi I. What’s New in Pigmentary Disorders. Dermatol Clin. 2019 Apr;37(2):175-181.
This website does not provide medical advice.
All information provided on this website, and on associated social media networks, including but not limited to texts, images, and numbers are for general information purpose only. It is not intended as medical advice and it does not include all possible precautions, side effects, or interactions that may occur. Neither NaturalLivingOnline.com nor its author/founder take responsibility for how you use this information. Statements contained on NaturalLivingOnline.com have not been evaluated by the FDA. You should conduct thorough research via multiple sources and consult your physician or qualified doctor before using any essential oil or herbal remedy. Information on NaturalLivingOnline.com must not be relied upon for medical, legal, financial or other decisions.