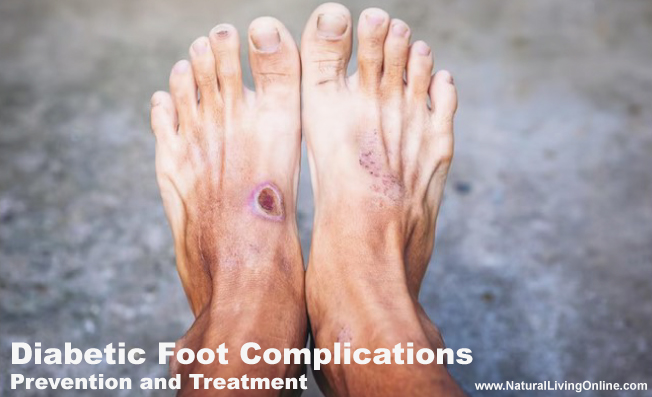
Diabetes is a chronic disease that affects millions of people worldwide. One of the common complications associated with diabetes is diabetic foot complications. Diabetic foot complications refer to a set of problems that affect the feet of individuals with diabetes, including neuropathy, peripheral arterial disease (PAD), and foot ulcers.
Recognizing the symptoms of diabetic foot complications is crucial for individuals with diabetes, as it can help prevent further nerve damage and serious complications such as amputation. Early detection and treatment of diabetic foot complications can significantly reduce the risk of severe outcomes and improve the quality of life for individuals with diabetes.
How does diabetes cause foot problems?
Diabetes can cause foot problems in several ways. The high blood sugar levels associated with diabetes can damage the nerves and blood vessels in the feet, leading to poor circulation, loss of sensation, and slow healing. This can increase the risk of foot injuries and infections, which can lead to serious complications if left untreated.
Diabetes can also cause changes in the skin and structure of the feet, making them more susceptible to injury and infection. For example, diabetes can cause the skin on the feet to become dry and cracked, which can lead to infections. Additionally, diabetes can cause changes in the bones and joints of the feet, leading to deformities such as hammertoes and bunions.
People with diabetes are also more prone to developing other conditions that can affect the feet, such as peripheral arterial disease (PAD) and neuropathy. PAD is a condition in which the arteries in the legs and feet become narrow or blocked, leading to poor circulation and an increased risk of foot ulcers and infections. Neuropathy is a condition in which the nerves in the feet and legs become damaged, leading to loss of sensation and an increased risk of injury and infections.
Diabetic Foot Complications
Diabetic Foot Complications are a common and serious complication of diabetes that can cause significant damage to the feet and legs. There are three types of diabetic foot complications that can occur, including neuropathy, peripheral arterial disease (PAD), and foot ulcers.
Neuropathy
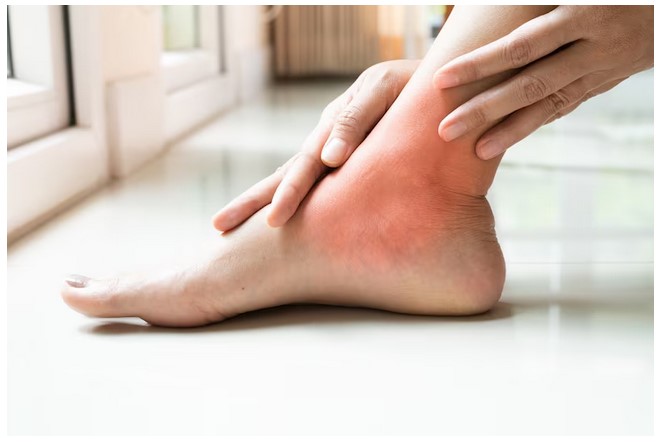
Neuropathy is a type of diabetic foot complication that affects the nerves in the feet and legs. The high blood sugar levels associated with diabetes can damage the nerves in healthy feet, leading to a loss of sensation in the feet and legs. This condition is known as diabetic neuropathy.
Symptoms:
- Numbness, tingling, or burning sensation in the feet and legs
- Loss of sensation or feeling in the feet and legs
- Muscle weakness or cramping
- Loss of balance or coordination
- Changes in the shape of the feet or toes
- Slow healing of wounds or infections in the feet and legs
Prevention and treatment:
Prevention of neuropathy involves maintaining healthy blood sugar levels through a healthy diet, regular exercise, and taking medication as prescribed by a doctor. Additionally, wearing proper footwear and practicing good foot hygiene can help prevent complications.
Treatment options for neuropathy include medication to manage pain, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes to manage blood sugar levels. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to repair damaged nerves.
Peripheral arterial disease (PAD)
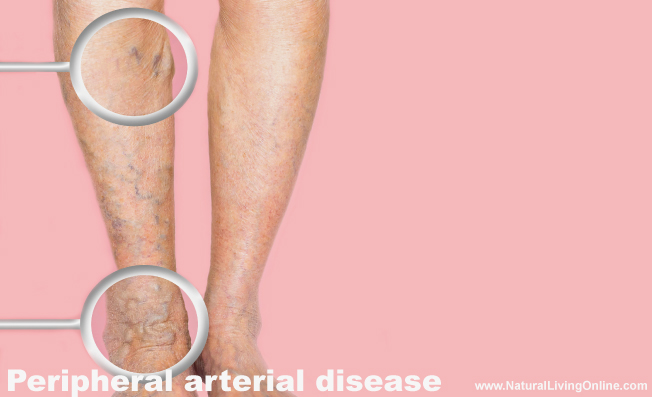
Peripheral arterial disease (PAD) is a type of diabetic foot complication that affects the blood vessels in the legs and feet. The high blood sugar levels associated with diabetes can cause the arteries to become narrow or blocked, leading to poor blood flow to the feet and legs.
Symptoms:
- Foot Pain or cramping in the legs or feet during activity
- Weakness or numbness in the legs or feet
- Sores or wounds on the legs or feet that do not heal
- Cold or discolored feet
Prevention and treatment:
Prevention of PAD involves maintaining healthy blood sugar levels through a healthy diet, regular exercise, and taking medication as prescribed by a doctor. Additionally, not smoking and managing other risk factors, such as high blood pressure and high cholesterol, can help prevent complications.
Treatment options for PAD include medication to manage symptoms, lifestyle changes to improve blood flow, and surgery to repair or bypass blocked arteries.
Foot ulcers
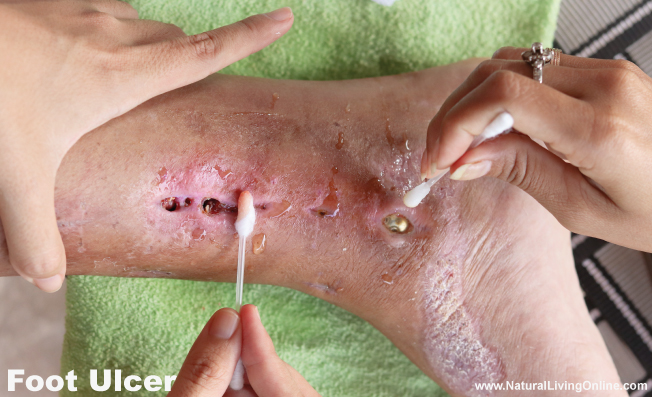
Foot ulcers are a type of diabetic foot complication that involves the development of open sores or wounds on the feet. The high blood sugar levels associated with diabetes can cause damage to the nerves and blood vessels in the feet, leading to poor circulation and slow healing.
Symptoms:
- Redness or swelling around the affected area
- An open sore or wound that does not heal
- Drainage from the affected area
- Pain or tenderness
Prevention and treatment:
Prevention of foot ulcers involves maintaining healthy blood sugar levels through a healthy diet, regular exercise, and taking medication as prescribed by a doctor. Additionally, practicing good foot hygiene, wearing proper footwear, and avoiding injury to the feet can help prevent complications.
Treatment options for foot ulcers include medication to manage pain and prevent infection, wound care to promote healing, and surgery in severe cases. Additionally, lifestyle changes may be necessary to improve blood sugar control and prevent further complications.
Prevention
Prevention is the key to avoiding diabetes related foot problems. Below are some ways to prevent diabetic foot problems:
Self-care measures:
diabetesFoot care and hygiene: People with diabetes should wash their feet every day with warm water and mild soap to keep feet healthy. They should dry their feet thoroughly, especially between the toes, and apply lotion or cream to keep the skin soft and supple. They should also check their feet daily for any cuts, blisters, or sores. Trim your toenails straight.
Proper footwear: For diabetes foot care you should wear proper footwear that fits well and provides adequate support and cushioning. Shoes should be comfortable and not cause any friction or pressure points. Diabetic shoes, custom orthotics, or inserts can be helpful for those with foot problems. Never walk barefoot. Not even at home! Always wear shoes or slippers and wear socks. You could step on something and get a scratch or cut.
Blood sugar control: Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels is crucial for preventing diabetic foot complications. People with diabetes should monitor their blood sugar regularly and follow their doctor’s recommendations for diet, exercise, and medication.
Regular check-ups:
People with diabetes should have their feet checked regularly by a foot doctor, at least once a year or more frequently if they have a history of foot problems. Regular foot exams can help detect any problems early and prevent complications. During a foot exam, the healthcare provider will check for any changes in skin color, temperature, sensation, and circulation, and look for any cuts, blisters, or sores.
Smoking cessation:
Smoking can worsen circulation problems and increase the risk of diabetic foot complications. Quitting smoking can help improve blood flow and reduce the risk of diabetes foot side problems. People with diabetes who smoke should talk to their healthcare provider about quitting options and support.
Natural Remedies for Diabetic Foot Care

Neglecting foot care can lead to various foot problems, including calluses, corns, blisters, and fungal infections. While there are many commercial products available for foot care, natural remedies can be an effective and affordable option. In this article, we will discuss some natural remedies for foot care.
Epsom Salt Foot Soak:
Epsom salt is a popular natural remedy for foot care. It contains magnesium sulfate, which helps to soothe sore muscles, reduce swelling, and promote relaxation. To use Epsom salt for foot care, add 1/2 cup of Epsom salt to a foot basin filled with warm water. Soak your feet in the hot water, for 15-20 minutes, then dry them thoroughly.
Vinegar Foot Soak:
Vinegar is another natural remedy for foot care. It has antifungal and antibacterial properties that can help to prevent athlete’s foot, fungal infections and foot odor. To use vinegar for foot care, add 1/2 cup of white vinegar to a foot basin filled with warm water. Soak your feet in the water for 15-20 minutes, then wash your feet and dry them thoroughly.
Tea Tree Oil Foot Soak:
Tea tree oil is a natural antifungal and antibacterial agent that can help to prevent fungal infections and foot odor. To use tea tree oil for foot care, add a few drops of tea tree oil to a foot basin filled with warm water. Soak your feet in the water for 15-20 minutes, then dry them thoroughly.
Coconut Oil Foot Massage:
Coconut oil is a natural moisturizer that can help to keep the skin on your feet soft and supple. To use coconut oil for foot care, warm a small amount of coconut oil in your hands, then massage it into your feet, focusing on any areas of dry or rough skin to protect your feet.
Aloe Vera Foot Mask:
Aloe vera is a natural skin-soothing agent that can help to reduce inflammation and moisturize the skin. To use aloe vera for foot care, mix 1/4 cup of aloe vera gel with 1/4 cup of coconut oil and 1/4 cup of oatmeal. Apply the mixture to take care of your feet, and let it sit for 10-15 minutes, then rinse off with warm water.
Baking Soda Foot Scrub:
Baking soda is a natural exfoliant that can help to remove dead skin cells and soften rough skin. To use baking soda for foot care, mix 1/4 cup of baking soda with a few drops of water to form a paste. Apply the paste to your feet and gently scrub in a circular motion, focusing on any areas of rough or dry skin. Rinse off with warm water.
Lavender Foot Soak:
Lavender is a natural relaxant that can help to soothe sore muscles and promote relaxation. To use lavender for foot care, add a few drops of lavender essential oil to a foot basin filled with warm water. Soak your feet in the water for 15-20 minutes, then dry them thoroughly.
In conclusion, diabetic foot complications are a serious and common problem for people with diabetes. These complications can lead to serious infections, amputations, and even death if left untreated. Recognizing the symptoms, seeking proper medical care, and taking preventative measures are key to reducing the risk of diabetic foot problems. Self-care measures such as proper foot hygiene, wearing comfortable shoes, and maintaining healthy blood sugar levels are crucial in preventing complications. Regular check-ups and quitting smoking are also important preventative measures. While natural remedies can provide some relief, they should not be used as a substitute for proper medical care. By taking care of their feet and working closely with their healthcare provider, people with diabetes can reduce their risk of foot problems and improve their overall health and quality of life.
References and Further Reading
Diabetic Foot Complications and Management – NIH
This website does not provide medical advice.
All information provided on this website, and on associated social media networks, including but not limited to texts, images, and numbers are for general information purpose only. It is not intended as medical advice and it does not include all possible precautions, side effects, or interactions that may occur. Neither NaturalLivingOnline.com nor its author/founder take responsibility for how you use this information. Statements contained on NaturalLivingOnline.com have not been evaluated by the FDA. You should conduct thorough research via multiple sources and consult your physician or qualified doctor before using any essential oil or herbal remedy. Information on NaturalLivingOnline.com must not be relied upon for medical, legal, financial or other decisions.