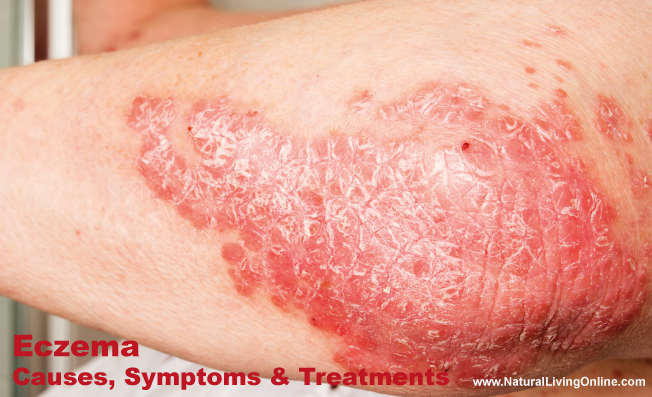
Eczema is a common skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Also known as atopic dermatitis, it is characterized by red, itchy, and inflamed skin. Eczema can be a chronic condition that can be challenging to manage, but there are ways to reduce symptoms and improve your quality of life. In this article, we will discuss the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for eczema.
Causes of Eczema
The exact cause of eczema is unknown, but it is believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors. People with a family history of eczema, allergies, or asthma are more likely to develop the condition. Environmental factors such as irritants, allergens, and stress can trigger or worsen eczema symptoms.
Clinical Signs and Symptoms
The signs and symptoms of eczema can vary from person to person, but some common ones include:
- Itchy, red, and dry skin: The skin affected by eczema can become very dry, itchy, and red.
- Thickened, scaly skin: Over time, the skin affected by eczema can become thickened and scaly, especially in areas that are frequently scratched.
- Blisters: In some cases, eczema can cause small blisters to form on the skin.
- Crusting: As eczema worsens, the skin can become crusted and oozing.
- Swollen skin: Eczema can cause the skin to become swollen, especially in areas like the hands and feet.
- Darkening or discoloration of the skin: The skin affected by eczema can become darker or lighter than the surrounding skin.
- Sensitivity to irritants: People with eczema may find that their skin is sensitive to certain irritants, such as soap or detergents.
- Infection: Because eczema can cause breaks in the skin, it can increase the risk of infection.
It’s important to note that not all of these symptoms may be present in every case of eczema, and some people may experience different symptoms. If you suspect you have eczema, it’s best to see a dermatologist for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
Treatment of Eczema
There is no cure for eczema, but there are several treatment options available to manage symptoms. The treatment options include:
- Topical Corticosteroids: Topical corticosteroids are anti-inflammatory medications that can be applied to the skin to reduce inflammation and itching. They are available in various strengths, and the appropriate strength will depend on the severity of the symptoms.
- Topical Calcineurin Inhibitors: Topical calcineurin inhibitors are a class of medications that can be used to reduce inflammation and itching. They are available in creams and ointments and can be used for long-term management of eczema.
- Moisturizers: Keeping the skin moisturized is key to preventing eczema. Apply a moisturizer to the skin regularly, especially after bathing, to lock in moisture.
- Antihistamines: Antihistamines are medications that can be used to reduce itching and promote sleep. They can be taken orally or applied topically to the skin.
- Wet Dressings: Wet dressings can be used to soothe and hydrate the skin. They involve wrapping the affected area in a wet bandage or dressing, which is then covered with a dry bandage or dressing.
- Light Therapy: Light therapy involves exposing the affected area to controlled amounts of ultraviolet light. It can help reduce inflammation and itching and is often used in combination with other treatments.
- Immunosuppressants: Immunosuppressants are medications that can be used to reduce the immune system’s response, which can reduce inflammation and itching. They are often used for severe cases of eczema.
Home Remedies
There are variety of home remedies that help alleviate the symptoms of eczema, although it is important to note that they are not a substitute for medical treatment. Here are some home remedies that may be helpful:
- Oatmeal baths: Adding colloidal oatmeal to a warm bath can help soothe itchy skin and reduce inflammation.
- Coconut oil: Applying coconut oil to affected areas can help moisturize the skin and reduce inflammation.
- Tea tree oil: Diluting tea tree oil with a carrier oil and applying it to affected areas may help reduce itching and inflammation.
- Apple cider vinegar: Diluting apple cider vinegar with water and applying it to affected areas may help reduce itching and inflammation.
- Aloe vera: Applying aloe vera gel to affected areas can help soothe and moisturize the skin.
- Turmeric: Mixing turmeric with a carrier oil and applying it to affected areas may help reduce inflammation and itching.
- Honey: Applying honey to affected areas may help moisturize and soothe the skin.
It is important to note that some people with eczema may have allergies or sensitivities to certain ingredients, so it is always a good idea to test a small area of skin before applying a new home remedy. Additionally, it is important to continue any prescribed medical treatments and to consult with a healthcare provider before using any new home remedies.
Prevention
Preventing eczema can be challenging, but there are steps you can take to reduce the likelihood of developing the condition or prevent flare-ups. Some tips for preventing eczema include:
- Avoid Triggers: Identify and avoid triggers that worsen your eczema. Common triggers include harsh soaps, detergents, fragrances, and certain foods.
- Use Mild Soaps and Cleansers: Use mild soaps and cleansers to avoid irritating the skin. Look for products that are fragrance-free, hypoallergenic, and formulated for sensitive skin.
- Keep the Skin Moisturized: Keep the skin moisturized by applying a moisturizer regularly, especially after bathing or washing the hands.
- Avoid Scratching: Avoid scratching the affected area, as this can worsen symptoms and lead to infection.
- Manage Stress: Stress can worsen eczema symptoms, so it is important to manage stress through relaxation techniques, exercise, and other stress-reducing activities.
- Wear Protective Clothing: Wear protective clothing such as gloves or long sleeves when working with harsh chemicals or when exposed to allergens.
- Maintain a Healthy Diet: Maintaining a healthy diet that is rich in nutrients can help support the immune system and reduce inflammation.
Conclusion
Eczema is a chronic skin condition that can be challenging to manage, but there are ways to reduce symptoms and improve your quality of life. The exact cause of eczema is unknown, but it is believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors. The symptoms of eczema can vary in severity and location and can be severe enough to affect a person’s quality of life. Treatment options for eczema include topical medications, moisturizers, antihistamines, wet dressings, light therapy, and immunosuppressants. Preventing eczema can be challenging, but there are steps you can take to reduce the likelihood of developing the condition or prevent flare-ups. By working with a healthcare provider and taking steps to prevent triggers, manage stress, and keep the skin moisturized, people with eczema can lead a healthy and comfortable life.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is eczema?
Eczema is a common skin condition characterized by red, itchy, and inflamed skin. It can occur on any part of the body, but is most common on the hands, feet, arms, and legs. Eczema can be chronic and long-lasting, and often flares up periodically.
What causes eczema?
The exact cause of eczema is not known, but it is believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Triggers can include allergens, irritants, stress, and changes in temperature or humidity.
Is eczema contagious?
No, eczema is not contagious and cannot be spread from person to person. However, scratching eczema lesions can cause the skin to become infected, which can then be spread.
How is eczema treated?
Treatment for eczema depends on the severity of the condition. Mild cases can often be managed with over-the-counter moisturizers and topical creams. More severe cases may require prescription creams or oral medications, such as corticosteroids or immunomodulators. It is important to work with a healthcare provider to develop an individualized treatment plan.
Can eczema be prevented?
While eczema cannot be prevented, there are steps that can be taken to minimize flare-ups and manage symptoms. These include avoiding triggers, such as harsh soaps and detergents, using fragrance-free and hypoallergenic products, keeping the skin moisturized, and managing stress. It is important to work with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized management plan.
References
- Mevorah B, Frenk E, Wietlisbach V, Carrel CF. Minor clinical features of atopic dermatitis. Evaluation of their diagnostic significance. Dermatologica. 1988;177(6):360-4.
- Kamińska E. [The role of emollients in atopic dermatitis in children]. Dev Period Med. 2018;22(4):396-403.
- Siegfried EC, Hebert AA. Diagnosis of Atopic Dermatitis: Mimics, Overlaps, and Complications. J Clin Med. 2015 May 06;4(5):884-917.
- Kim JP, Chao LX, Simpson EL, Silverberg JI. Persistence of atopic dermatitis (AD): A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016 Oct;75(4):681-687.e11.
This website does not provide medical advice.
All information provided on this website, and on associated social media networks, including but not limited to texts, images, and numbers are for general information purpose only. It is not intended as medical advice and it does not include all possible precautions, side effects, or interactions that may occur. Neither NaturalLivingOnline.com nor its author/founder take responsibility for how you use this information. Statements contained on NaturalLivingOnline.com have not been evaluated by the FDA. You should conduct thorough research via multiple sources and consult your physician or qualified doctor before using any essential oil or herbal remedy. Information on NaturalLivingOnline.com must not be relied upon for medical, legal, financial or other decisions.