A tropical fruit with a rough, scaly skin and a crown of spiky green leaves on top. The edible part of the pineapple is the fleshy, fibrous flesh that is yellow or orange in color.
Pineapples are a nutritious fruit with a variety of medicinal properties and health benefits. They contain high levels of vitamin C and manganese, as well as other essential nutrients such as vitamins B1, B6, and E, potassium, copper, magnesium, and folate. These nutrients contribute to the fruit’s anti-inflammatory effects, potential cancer-fighting properties, digestive health benefits, immune system boost, and positive effects on cardiovascular health. Pineapples also have several health benefits, including aiding in weight loss, improving vision, strengthening bones, providing relief from allergies and asthma, improving digestion, and reducing the risk of macular degeneration and cataracts.
Botanical Profile
Botanical Name: Ananas comosus
Common Names: Pineapple, ananas
Plant Family: Bromeliaceae
Countries of origin: Pineapples are native to South America and were introduced to other tropical regions by the Europeans in the 16th century. Today, pineapples are grown in many tropical countries around the world.
Parts Used: The fruit of the pineapple plant. The fruit is rich in vitamins and minerals, while the leaves contain bromelain, an enzyme with anti-inflammatory effects.
Therapeutic Properties: cancer-fighting properties, digestive health benefits, immune system boost, and positive effects on cardiovascular health. Pineapples also have several health benefits, including aiding in weight loss, improving vision, strengthening bones, providing relief from allergies and asthma, improving digestion, and reducing the risk of macular degeneration and cataracts.
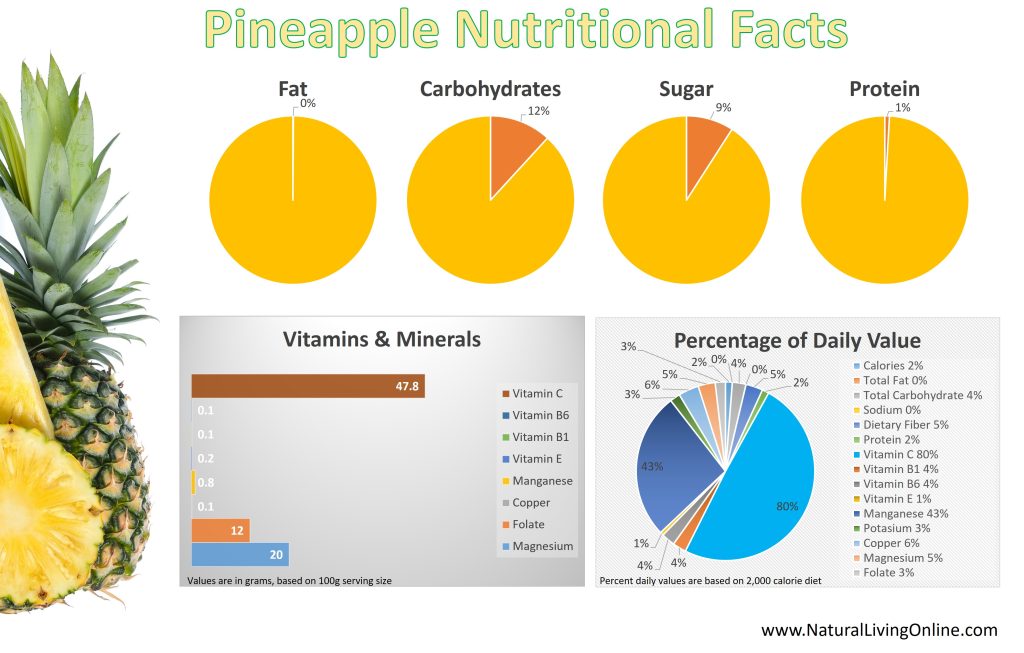
Nutritional Content of Pineapples
Pineapples are a good source of vitamin C, providing about 130% of the recommended daily value in a single serving. Vitamin C is a powerful antioxidant that helps to protect cells from damage caused by free radicals. Pineapples are also a good source of manganese, providing about 76% of the recommended daily value in a single serving. Manganese is an essential mineral that plays a role in several enzymatic reactions in the body, including the metabolism of carbohydrates and the synthesis of proteins and collagen.
In addition to vitamin C and manganese, pineapples are also a good source of several other essential nutrients. These include vitamins B1, B6, and E, potassium, copper, magnesium, and folate.
Vitamin B1 (thiamin) helps to convert carbohydrates into energy, while vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) is important for the synthesis of neurotransmitters and the metabolism of proteins and carbohydrates.
Vitamin E is an antioxidant that helps to protect cells from damage caused by free radicals.
Potassium is an electrolyte that helps to regulate the balance of fluids in the body and is important for the proper functioning of muscles and nerves.
Copper is an essential trace element that is involved in the synthesis of collagen and the metabolism of iron.
Magnesium is an essential mineral that is involved in more than 300 enzymatic reactions in the body, including the metabolism of energy and the synthesis of proteins and nucleic acids.
Folate is a B-vitamin that is important for the synthesis of DNA and the proper functioning of the immune system.
Medicinal Properties
- Anti-inflammatory effects: Pineapples contain a group of enzymes called bromelain, which has been shown to have anti-inflammatory effects. Bromelain has been shown to reduce swelling, inflammation, and pain in people with osteoarthritis and other inflammatory conditions.
- Potential cancer-fighting properties: Some research suggests that pineapples may have potential cancer-fighting properties due to their high levels of antioxidants and other nutrients. However, more research is needed to confirm these effects and to determine the optimal dosage and duration of treatment.
- Digestive health benefits: Pineapples are a good source of dietary fiber, which helps to promote regular bowel movements and prevent constipation. The bromelain in pineapples may also help to break down proteins and improve digestion.
- Boost to immune system: Pineapples are a good source of vitamin C, which is important for the proper functioning of the immune system. Vitamin C helps to protect cells from damage caused by free radicals and helps to stimulate the production of white blood cells, which are important for fighting off infections.
- Cardiovascular health: Some research suggests that pineapples may have positive effects on cardiovascular health. The high levels of vitamin C and manganese in pineapples may help to reduce the risk of heart disease by lowering blood pressure, decreasing oxidative stress, and improving cholesterol levels.
Health Benefits of Pineapples
- Weight loss aid: Pineapples are low in calories and high in fiber, which makes them a good choice for people looking to lose weight. The fiber in pineapples helps to promote feelings of fullness and can help to reduce the total number of calories consumed.
- Improved vision: The high levels of vitamin C in pineapples may help to improve vision and reduce the risk of age-related eye conditions such as cataracts and macular degeneration.
- Stronger bones: Pineapples are a good source of manganese, which is important for the proper metabolism of calcium and the synthesis of collagen. Collagen is an important component of bone tissue, and adequate intake of manganese may help to improve bone density and reduce the risk of osteoporosis.
- Relief from allergies and asthma: Some research suggests that the bromelain in pineapples may help to reduce inflammation and improve symptoms of allergies and asthma. However, more research is needed to confirm these effects and to determine the optimal dosage and duration of treatment.
- Improved digestion: The high levels of fiber in pineapples and the digestive-aiding effects of bromelain make pineapples a good choice for improving digestion.
- Reduced risk of macular degeneration and cataracts: The high levels of vitamin C in pineapples may help to reduce the risk of age-related eye conditions such as macular degeneration and cataracts.
Side Effects and Contraindications
Pineapples are generally considered safe to consume and have few known side effects. However, there are some potential side effects and contraindications to be aware of:
- Allergic reactions: Some people may have an allergic reaction to pineapples, which can cause symptoms such as skin rash, hives, itching, swelling, difficulty breathing, and anaphylaxis. If you have a known allergy to pineapples or other tropical fruits, you should avoid consuming them.
- Drug interactions: Bromelain, an enzyme found in pineapples, may interact with certain medications and may cause them to be less effective. For example, bromelain may interfere with the absorption of certain antibiotics, blood thinners, and anti-inflammatory drugs. If you are taking any medications, you should talk to your healthcare provider before adding pineapples to your diet.
- Upset stomach: Consuming large amounts of pineapples may cause upset stomach, bloating, and diarrhea in some people. If you experience these symptoms after consuming pineapples, you should reduce your intake or avoid consuming them.
- Pregnancy: There is limited information on the safety of consuming pineapples during pregnancy. Some sources suggest that consuming large amounts of pineapples may cause uterine contractions and may increase the risk of miscarriage. However, more research is needed to confirm these effects. If you are pregnant or planning to become pregnant, you should talk to your healthcare provider before consuming pineapples.
It is important to note that these are potential side effects and contraindications, and they may not apply to everyone. If you have any concerns about consuming pineapples, you should talk to your healthcare provider.
Conclusion
Pineapples are a nutritious fruit with a variety of medicinal properties and health benefits. They are a good source of vitamin C and manganese, as well as other essential nutrients such as vitamins B1, B6, and E, potassium, copper, magnesium, and folate. These nutrients contribute to the fruit’s anti-inflammatory effects, potential cancer-fighting properties, digestive health benefits, immune system boost, and positive effects on cardiovascular health. Pineapples also have several health benefits, including aiding in weight loss, improving vision, strengthening bones, providing relief from allergies and asthma, improving digestion, and reducing the risk of macular degeneration and cataracts.
References:
- Pineapple (Ananas comosus): A comprehensive review of nutritional values, volatile compounds, health benefits, and potential food products
- Properties and Therapeutic Application of Bromelain: A Review
- Bromelain, a Group of Pineapple Proteolytic Complex Enzymes (Ananas comosus) and Their Possible Therapeutic and Clinical Effects. A Summary
This website does not provide medical advice.
All information provided on this website, and on associated social media networks, including but not limited to texts, images, and numbers are for general information purpose only. It is not intended as medical advice and it does not include all possible precautions, side effects, or interactions that may occur. Neither NaturalLivingOnline.com nor its author/founder take responsibility for how you use this information. Statements contained on NaturalLivingOnline.com have not been evaluated by the FDA. You should conduct thorough research via multiple sources and consult your physician or qualified doctor before using any essential oil or herbal remedy. Information on NaturalLivingOnline.com must not be relied upon for medical, legal, financial or other decisions.













